Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Generic Medicine
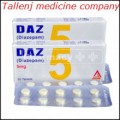
- Generic Diazepam DAZ 10mg by Safe-Pharma x 10 Blisters
Product Description
Type a description for this product here...
Product Description
Indications:
Diazepam is mainly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal. It is also used as a premedication for inducing sedation, anxiolysis or amnesia before certain medical procedures (e.g., endoscopy).
Intravenous diazepam or lorazepam are first line treatments for status epilepticus; However, lorazepam has advantages over diazepam including a higher rate of terminating seizures and a more prolonged anticonvulsant effect. Diazepam is rarely used for the long-term treatment of epilepsy because tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects of diazepam usually develops within 6 to 12 months of treatment, effectively rendering it useless for this purpose. Diazepam is used for the emergency treatment of eclampsia, when IV magnesium sulfate and blood pressure control measures have failed. However, benzodiazepines such as diazepam can be used for their muscle relaxant properties to alleviate pain which is caused by muscle spasms, caused by various dystonias, including blepharospasm Tolerance often develops to the muscle relaxant effects of benzodiazepines such as diazepam. Baclofen or tizanidine is sometimes used as an alternative to diazepam. Tizanidine has been found to be equally effective as other antispasmodic drugs and have superior tolerability than baclofen and diazepam. Benzodiazepines do not have any pain relieving properties of themselves and are generally recommended to be avoided in individuals with pain.
The anticonvulsant effects of diazepam, can help in the treatment of seizures, due to a drug overdose or chemical toxicity as a result of exposure to sarin, VX, soman (or other organophosphate poisons; See #CANA), lindane, chloroquine, physostigmine, or pyrethroids Diazepam is sometimes used intermitently for the prophylaxis of febrile seizures which occur as a result of a high fever in children and neonates under 5 years of age. Long-term use of diazepam for the management of epilepsy is not recommended; however, a subgroup individuals with treatment resistant epilepsy benefit from long-term benzodiazepines and for such individuals clorazepate has been recommended due to its slower onset of tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects.
Diazepam has a broad spectrum of indications (most of which are off-label), including:
- Treatment of anxiety, panic attacks, and states of agitation
- Treatment of neurovegetative symptoms associated with vertigo
- Treatment of the symptoms of alcohol, opiate and benzodiazepine withdrawal
- Short-term treatment of insomnia
- Treatment of tetanus, together with other measures of intensive-treatment
- Adjunctive treatment of spastic muscular paresis (para-/tetraplegia) caused by cerebral or spinal cord conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury (long-term treatment is coupled with other rehabilitative measures)
- Palliative treatment of stiff person syndrome
- Pre-/postoperative sedation, anxiolysis and/or amnesia (e.g., before endoscopic or surgical procedures)
- Treatment of complications with hallucinogens, such as LSD or overdose of CNS stimulants, such as cocaine, or methamphetamine.
- Prophylactic treatment of oxygen toxicity during hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Veterinary uses:
- Diazepam is used as a short-term sedative and anxiolytic for cats and dogs. It is also used for short-term treatment of seizures in dogs and short-term and long-term treatment of seizures in cats. It can also be used as an appetite stimulant. For emergent treatment of seizures, the typical dose is 0.5 mg/kg intravenously, or 1–2 mg/kg of the injectable solution administered in the rectum.
Before judicial executions:
- The State of California offers diazepam to condemned inmates as a pre-execution sedative as part of their Lethal Injection program.
Dosage:
Dosages should be determined on an individual basis, depending upon the condition to be treated, the severity of symptoms, the body weight of the patient, and any comorbid conditions the patient may have.
Typical dosages for healthy adults range from 2 mg per dose to 10 mg per dose taken 2 to 4 times per day, depending on such factors as body weight and condition being treated. For the elderly or people with liver disorders, initial dose is at the low en